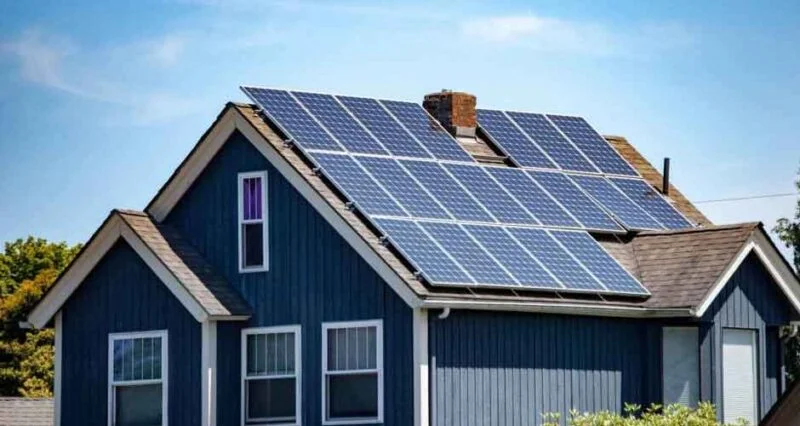
Residential solar electricity has gained significant traction as a sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources. Embraced for its environmental benefits and potential cost savings, solar power offers homeowners a promising avenue toward energy independence. Like any technology, it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages that prospective adopters should carefully consider. For example, the growing affordability of solar panel installations has made them more accessible to a broader range of homeowners. As more households embrace renewable energy solutions, the solar power industry is poised for continued growth and innovation.
Advantages of Residential Solar Electricity
One of the primary advantages of residential solar electricity is its eco-friendliness. Solar energy is renewable and abundant, harnessing the power of the sun to generate electricity without producing greenhouse gases or other harmful emissions. This clean energy source contributes to reducing carbon footprints and mitigating climate change impacts. Furthermore, solar panels have a relatively low environmental impact during their operational lifespan compared to fossil fuel-based power generation. Solar installations can also help communities achieve resilience against power outages, benefiting both homeowners and local economies.
Financial benefits also play a crucial role in the appeal of solar power. By generating electricity on-site, homeowners can potentially lower their utility bills over time. With proper installation and optimal sunlight exposure, solar panels can generate enough electricity to meet a substantial portion of a household’s energy needs, thereby reducing reliance on grid-supplied electricity. Various financial incentives and rebates offered by governments and utilities can further offset initial installation costs and accelerate the return on investment for solar energy systems. Moreover, the resale value of homes equipped with solar panels tends to be higher, providing additional financial benefits to homeowners.
Another advantage lies in energy independence. Solar power allows homeowners to generate their own electricity, reducing dependency on external energy providers and insulating themselves from fluctuating energy prices. This autonomy is particularly appealing during times of energy shortages or disruptions, providing a reliable source of power. Furthermore, solar energy systems often come with warranties that cover maintenance and repairs, ensuring prolonged reliability and peace of mind for homeowners. Additionally, integrating battery storage with solar installations can enhance energy independence by storing excess electricity for use during periods of low sunlight or high demand. When considering residential solar electricity, searching for a “solar consultant nearby” to speak with can provide valuable insights into system options, costs, and local regulations, ensuring a tailored and efficient installation process.
Disadvantages of Residential Solar Electricity
Despite its benefits, residential solar electricity also presents some challenges. One notable drawback is the initial cost of installation. While solar technology costs have decreased in recent years, the upfront investment for purchasing and installing solar panels can still be substantial. However, various financing options, including leases and loans, are available to help reduce this initial expense. In addition, homeowners should consider the potential variability in energy savings based on factors such as local climate and energy usage patterns when evaluating the long-term financial benefits of solar installations.
Another consideration is the variability of solar energy production. Solar panels rely on sunlight to generate electricity, meaning their output can fluctuate based on weather conditions and seasonal changes. This variability may necessitate alternative energy sources or energy storage solutions to ensure consistent power supply, particularly during periods of low sunlight. Plus, advancements in battery storage technology offer homeowners the option to store excess solar energy for use during peak demand or when sunlight is limited. Integrating smart energy management systems can further optimize energy usage and reduce reliance on grid-supplied electricity during periods of solar energy variability.
Maintenance is another factor to consider. While solar panels generally require minimal maintenance, occasional cleaning and inspections are necessary to ensure optimal performance. Moreover, the lifespan of solar panels, typically ranging from 25 to 30 years, may require eventual replacement or upgrades, adding to long-term costs. Homeowners can extend the lifespan of their solar panels by investing in high-quality materials and professional installation services. Regular monitoring of energy production through online tools or apps can also help identify any potential maintenance issues early, ensuring efficient operation throughout the panel’s lifespan.
Shining a Light on the Future of Residential Solar Electricity
Residential solar electricity offers a compelling solution for homeowners looking to embrace sustainable energy practices and reduce their carbon footprint. The advantages, including environmental benefits, potential cost savings, and energy independence, make it a viable choice for many households. However, it’s essential to weigh these benefits against the upfront costs, variability in energy production, and maintenance requirements associated with solar power systems. As the demand for renewable energy grows, advancements in technology and supportive policies are likely to enhance the affordability and efficiency of solar electricity systems. By carefully evaluating these factors, homeowners can make informed decisions about integrating solar power into their homes, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future.