
The electrical grid faces growing threats like cyber attacks and climate change. According to the Department of Energy, U.S. power outages cost the economy up to $70 billion annually. To strengthen resilience, the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) created the Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) standards.
These legally binding rules enhance cybersecurity and the overall reliability of the grid. In this article let us look at how the NERC CIP standards strengthen the energy infrastructure resilience against challenges.
NERC CIP Standards: Embedding Resilience into Grid Infrastructure
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) makes rules called standards to help keep the electrical grid working properly. The Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) standards are a set of rules made by NERC to improve how power companies protect important equipment from cyber attacks and other problems.
Power companies have to follow the CIP standards. If they don’t, they can get in trouble. The standards tell the companies exactly what they need to do to keep their systems safe. For example, the standards say companies have to identify their most important cyber assets. These are things like computers that control the flow of electricity. Companies need to take extra steps to protect these assets from hackers.
Another NERC CIPs standards says companies have to limit who can access certain systems. For example, they should only let employees use cyber assets if they need them to do their jobs. This helps prevent unauthorized people from getting into places they shouldn’t.
Some CIP standards also require background checks for employees before giving them access. And companies need to have plans in place for responding quickly if an attack does happen.
By following the CIP standards, power companies can better prevent cyber attacks or other problems. This makes the electric grid more reliable and resilient. The standards help create a safer and more secure power system.
Augmenting Grid Reliability
The electrical grid is a big, complex system made up of power plants, transmission lines, and local utilities that distribute electricity to homes and businesses. Keeping all these parts working smoothly together is a big job. There are many things that can cause problems and lead to power outages.
To help improve grid reliability, modern technology is being added to augment or enhance the way the system works. For example, smart sensors are being installed to monitor equipment. The sensors can detect issues early before they become big problems.
Grid operators are also using more automation, like remotely controlled switches. This allows them to reroute power and restore service faster when outages occur. Operators can even use automation to anticipate problems and take preventative steps.
Advanced computer models help operators better understand what’s happening on the grid in real-time. And improved weather forecasting helps them prepare for severe storms that could damage equipment.
Another technology that helps augment grid operations is energy storage, like big batteries. They can store electricity and release it when needed to smooth out supply and demand.
By using modern technologies like sensors, automation, computer models, and energy storage, grid operators can detect problems sooner, respond faster, and prevent many outages. This improves the overall reliability of the electric system.
Compliance Rigor & Continuous Enhancement
Power companies have to follow many rules and regulations to keep the electrical grid working properly. These rules are called compliance requirements. Some important ones are reliability standards from the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC).
The NERC standards help make sure power companies are doing things to prevent blackouts and other issues. Companies need to prove they are complying by collecting lots of data and paperwork. NERC sometimes audits companies to check they are following the rules. Look at the violations of NERC CIP over the years:
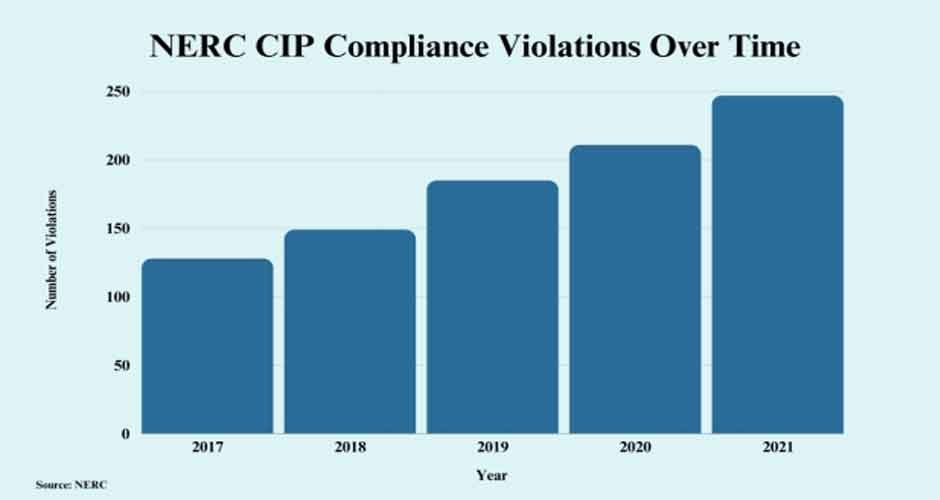
If NERC finds problems, they can penalize companies with big fines. So utilities have to be rigorous about compliance. They set up strong programs to meet all the requirements. Compliance teams track progress and report to management.
But compliance isn’t just about following the letter of the rules. The spirit behind the standards is promoting reliability. So leading utilities don’t just comply – they continuously look for ways to go above and beyond.
They regularly re-evaluate their assets, processes, and procedures. They upgrade equipment, improve training, and invest in new technology. A rigorous compliance mindset drives continuous enhancement.
This creates a culture of excellence. Employees are encouraged to find innovative ways to boost reliability, not just meet minimum standards. Rigorous compliance and continuous enhancement make the grid more robust and resilient.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do NERC CIP standards address emerging threats like cyberattacks?
By continually revising CIP requirements to address evolving attack vectors, NERC standards help utilities target contemporary threats like ransomware, phishing, and supply chain compromises based on the latest threat intelligence. Mandatory periodic risk assessments also reveal newfound vulnerabilities to inform standards development.
What steps can energy companies take to ensure compliance with NERC CIP standards?
Utilities should assemble cross-disciplinary teams with clear compliance responsibilities to integrate standards into budgets, policies, and procedures. Regular self-assessments help spot gaps while training ensures employee proficiency in managing vulnerabilities. Further, liaising with regulators during audits enables smooth remediation of any deficiencies through corrective action plans overseen by NERC.
Are there any notable examples of energy infrastructure resilience being tested and improved through NERC CIP standards?
Hurricane Sandy in 2012 unleashed valuable lessons about hybrid threats and interdependency risks while demonstrating NERC CIP’s effectiveness in restoration, ultimately driving standards expansion. Later in 2021, standards helped contain vulnerabilities exposed by major cyber incidents abroad. Such episodes validate standards efficacy while guiding continuous enhancement to keep pace with intensifying risks.
Conclusion
Through mandatory standards, compliance oversight, and a culture of continuous enhancement, NERC promotes resilience across North American energy infrastructure. As emerging technologies and threats continue to evolve, the CIP standards provide a flexible and proactive framework to manage risk and secure our critical electricity services. Adherence to the standards requires commitment and investment from utilities but helps ensure reliable power for homes, businesses, and critical services. Overall, the CIP program is a cornerstone for building grid resilience now and into the future.

