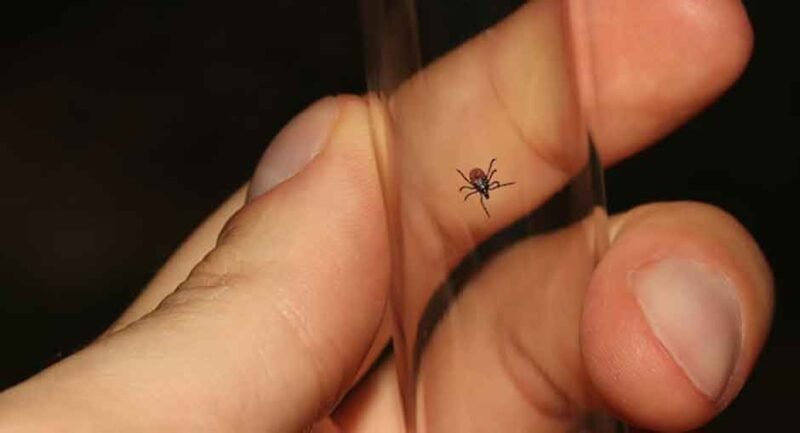
Originating from the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi and transmitted via tick bites, Lyme disease has become a noteworthy global health concern. Untreated, this condition has the potential to lead to severe complications impacting the joints, heart, and nervous system. Prompt and suitable treatment is vital for symptom management and preventing long-term consequences. This article explores five treatment approaches individuals with Lyme disease may consider under the guidance of healthcare professionals.
1. Antibiotic Therapy:
The most common and widely accepted treatment for Lyme disease involves antibiotics, with oral medications like doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime proving effective in early-stage cases by eliminating the infection-causing bacteria. The choice and duration of antibiotics hinge on disease stage and individual factors.
Completing the full antibiotic course, as prescribed, is crucial for complete eradication. In advanced cases, intravenous (IV) antibiotics may be recommended for a more direct and potent delivery into the bloodstream.
Rigorous monitoring and treatment plan adjustments by healthcare professionals are essential to ensure optimal efficacy, minimize potential side effects, and tailor the approach to individual patient needs.
2. Herbal and Alternative Therapies:
Some individuals may explore complementary therapies alongside or instead of traditional antibiotics. Botanicals such as Japanese knotweed, cat’s claw, and garlic are under investigation for their potential antimicrobial properties.
Furthermore, ongoing research explores alternative therapies, including hyperbaric oxygen therapy, acupuncture, and dietary modifications, for their potential in managing symptoms.
However, their effectiveness remains inconclusive, and they are recommended as supplementary options rather than primary treatments. As research progresses, ongoing scrutiny of these alternative approaches is essential for a comprehensive understanding of their role in Lyme disease management.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Medications:
Effectively managing inflammation is a cornerstone of Lyme disease treatment. Employing anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen contributes to alleviating pain and reducing inflammation.
In instances of severe inflammation and swelling, healthcare professionals may recommend potent corticosteroids. However, their usage requires vigilant monitoring due to potential side effects and the risk of immune system suppression.
Striking a careful balance in the administration of these medications is paramount, ensuring their benefits outweigh potential drawbacks in the comprehensive management of Lyme disease.
Regular medical oversight remains crucial for a nuanced and personalized approach to inflammation control, emphasizing the importance of individualized treatment plans aligned with the patient’s specific health profile.
4. Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation:
Lyme disease may induce joint pain, muscle aches, and fatigue, markedly affecting an individual’s mobility and overall quality of life. The pivotal role of physical therapy and rehabilitation becomes evident in the restoration of function, alleviation of pain, and enhancement of overall well-being.
Personalized exercise programs, thoughtfully crafted by skilled physical therapists, concentrate on not only strengthening muscles, enhancing joint flexibility, and boosting endurance but also fostering a supportive environment for the individual’s mental and emotional resilience.
These rehabilitation techniques, meticulously tailored, not only manage pain but also improve coordination, assisting individuals in regaining independence and facilitating a smoother return to their daily activities.
The collaborative effort between patients and physical therapists in these tailored programs serves as a cornerstone in the holistic approach to Lyme disease management, ensuring comprehensive care for both the physical and emotional aspects of the individual’s well-being.
5. Emerging Therapeutic Frontiers: Investigating the Role of Stem Cells for this Disease
Recent breakthroughs in medical research have stimulated curiosity surrounding the exploration of stem cells for Lyme disease. This innovative avenue holds promise for developing novel therapeutic interventions, leveraging the regenerative capacities of stem cells to address the complexities of Lyme disease management.
By harnessing the unique ability of stem cells to differentiate into various cell types, researchers aim to not only combat the infection directly but also to promote tissue repair and alleviate persistent symptoms, offering new hope for individuals navigating the challenges of Lyme disease. Rigorous clinical studies are underway to further elucidate the effectiveness and safety of this cutting-edge approach.
Conclusion:
A thorough treatment plan addressing the illness’s mental and physical aspects is necessary for the management of Lyme disease. The discussed treatment plans – antibiotic therapy, herbal and alternative therapies, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy and rehabilitation, and supportive therapies for mental health – offer diverse options. Close collaboration with healthcare professionals ensures the development of a personalized treatment plan, addressing the unique needs of each individual and maximizing the effectiveness of Lyme disease management.